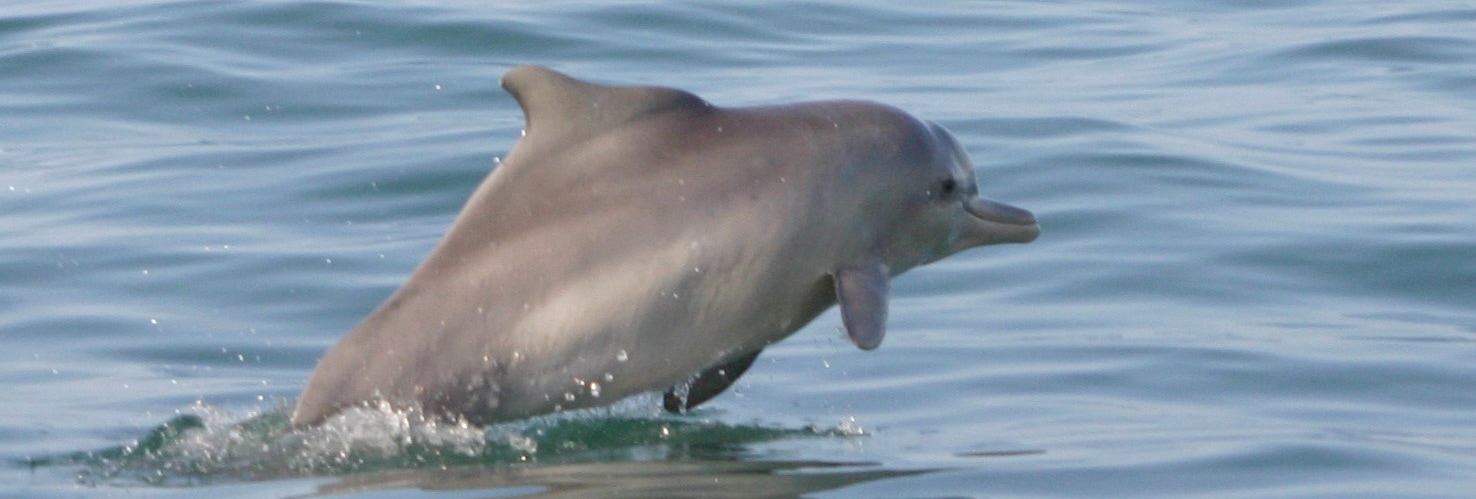
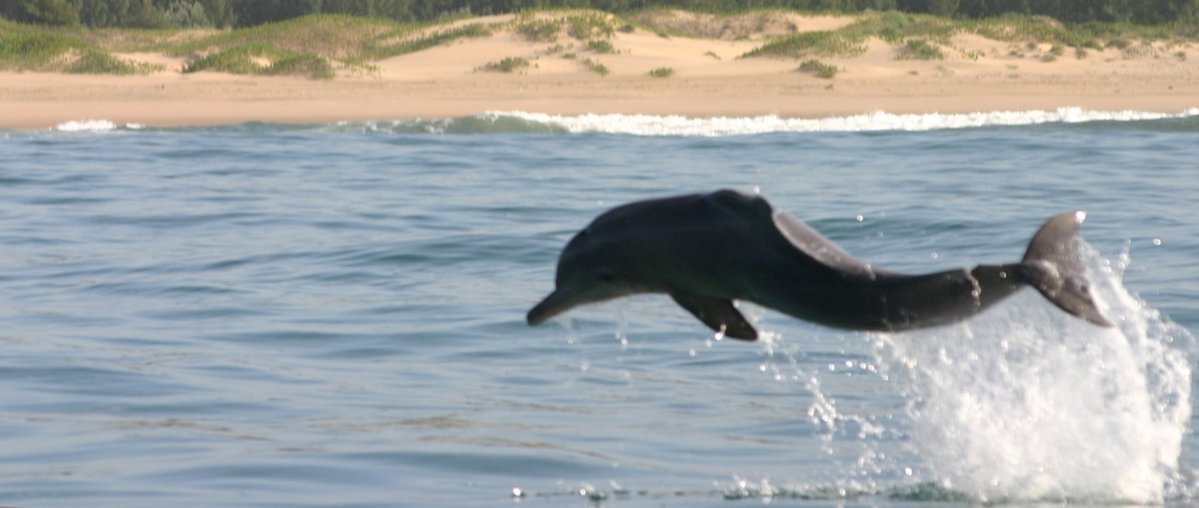
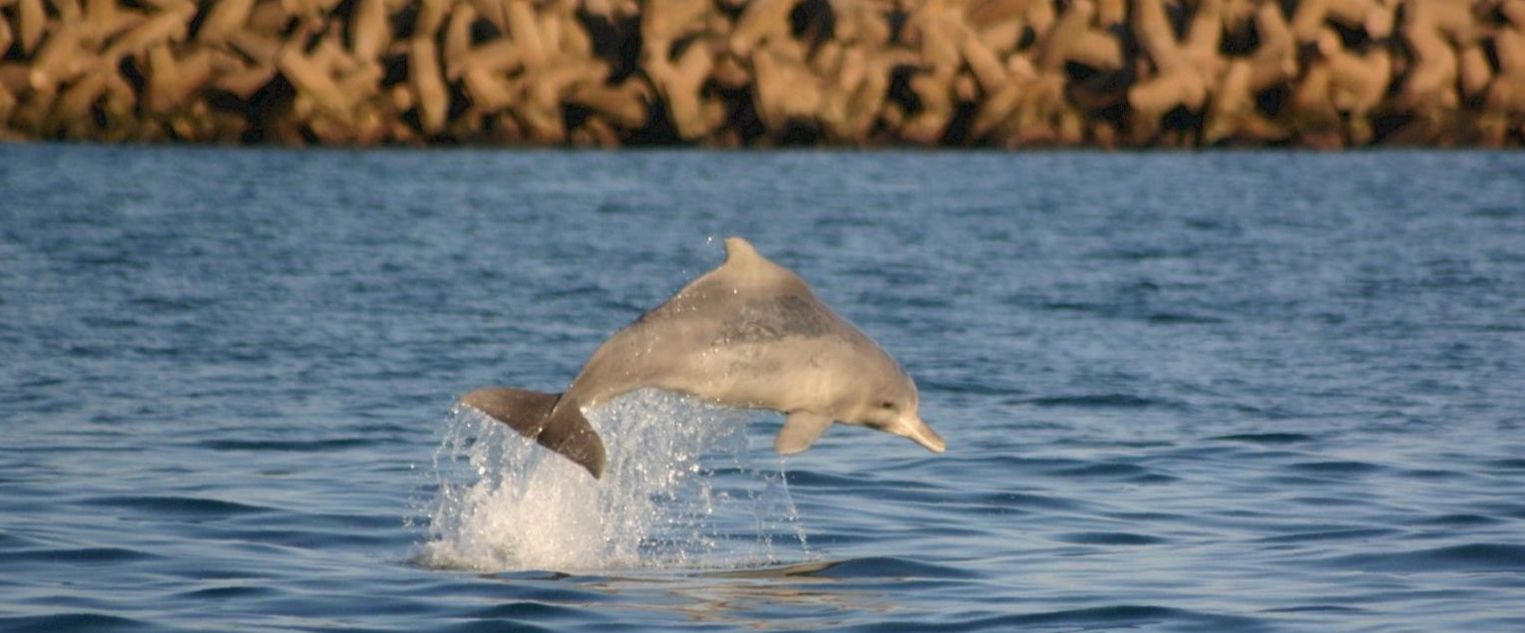
This is a rare species of dolphin and most people have never even heard of a humpback dolphin before and there just don’t seem to be many of them around. Unlike their bottlenose dolphin cousins they are shy and usually avoid boats and people.
|
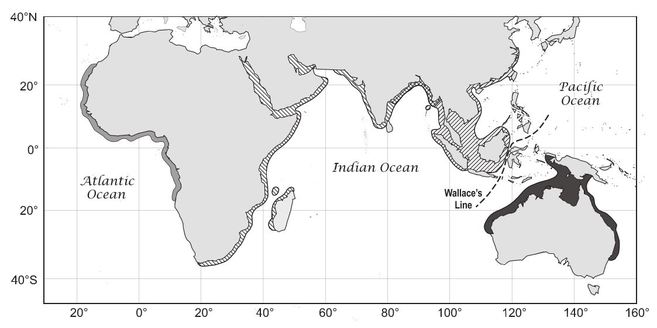
Indian Ocean humpback dolphins are found in a narrow strip of shallow, coastal waters from False Bay, South Africa along the coastal waters of South, East and North Africa, and the Middle East to approximately the southern tip of India and possibly further east. Diagram from Jefferson & Rosenbaum (2014). |
They inhabit a narrow band of shallow (<25m) water, close to the coast often near estuaries. In KwaZulu-Natal, they appear to be concentrated on the Thukela Bank between the mouth of the Thukela River and St. Lucia on a wider-than-normal part of the very narrow “Natal inshore” ecozone.
Humpback dolphins are not very fussy eaters and consume a wide variety of nearshore, estuarine, and reef fishes. Studies of the stomach contents of the humpback dolphins that died in the shark nets showed that they mostly eat:
It’s really interesting that many of these fish make noises (like grunts and burps) which suggests that the dolphins listen for their prey (rather than looking), which is very useful in Richards Bay’s brown water!
- ribbon fish (Trichiurus lepturus)
- bearded croaker (Johnius amblycephalus)
- glassnosed anchovy (Thryssa vitrirostris)
- olive grunter (Pomadasys olivaceum)
- squid (Loligo spp)
It’s really interesting that many of these fish make noises (like grunts and burps) which suggests that the dolphins listen for their prey (rather than looking), which is very useful in Richards Bay’s brown water!
At Richards Bay, the harbour entrance is a core feeding area for humpback dolphins and the shipping lane (used by all the big, commercial ships and smaller ski-boats) goes right through the middle. This is bad news for humpback dolphins and means that they are exposed to a variety of threats, for example, chemical pollution (because of land-based runoff), noise pollution, boat disturbance and food-web changes due to exotic species.